
My Sale Extended and Woodland birds in Donegal




One of the joys of acrylic gouache is that it dries very quickly and is opaque – so it lends itself to this sort of mark making.

Dun Fhraoigh in Irish means, “Fort of the Heather” – it has been a fort at Dunree for thousands of years, since the Bronze age (over 4000 years ago). When you see the chunk of rock that the “modern” day fort (well Napoleonic era) for has been built on, you understand why.
Its a big chunk of rock! (photo credit: Emma Cownie)
Its location, on the cliffs of Dunree Head, is great for observing and controlling ships moving up and down the majestic Lough Swilly, one of Ireland’s three glacial fjords.
The English built this sturdy fort on the chunk of rock c. 1812-3 with a draw-bridge! The enemy back then, as readers of Jane Austen will know, was the French forces of Napolean Bonaparte. (The story of Jane Austen’s Donegal nieces is worthy of a BBC/RTE mini-series in its own right; linking Kent, Ramelton and Gweedore). The French had attempted landing in Lough Swilly in 1798 with a force of about 8,000 men, which was repelled at sea. The Royal Navy anchored ships in the Lough. There were a lot of big guns here, nine 24-pounders were in 1817. There was once a Martello-type in the centre of the old fort but it was demolished c. 1900, as it obstructed the field of fire from the new fort on the summit of Dunree Hill.
Although the Irish Free State was created in 1922 and they followed (and still follow) a policy of political neutrality, the British army did not leave Dunree until 1938. This was because Lough Swilly was a “Treaty Port”, and it remained under British military control for defensive purposes. During the Second World War, it was under control of the Irish Army and it played an integral role in safeguarding Ireland when a number of anti aircraft guns were added to site. The waters off the coast of Donegal are under threat today from Russia’s so-called “shadow fleet”.
I am not particularly interested in military hardware, although I know plenty of people in the world are. I have not been in the military museum. What did take my interest, however, were the barracks. There were brick buildings but also a lot of decaying iron huts that the gunners had lived in. I am nosy and I enjoy seeing how people lived. Although, frustratingly, most of that has gone. There tiny glimpses; brick chimney stacks, the odd rusting bedstead but not a lot.











A little further up (a steep) hill from Fort Dunree and the barrack buildings is Dunree Lighthouse. This a puzzling lighthouse. I am used to lighthouses being built atop of great pillars like the one across the Swilly water at Fanad.
The one at Dunree, however, has no tower. It doesnt need one. The light is at ground level. The “ground” however its up high on the cliff way above the Fort. A lantern attached to a house for the Lighthouse Keeper was built, and the light established on 15th January 1876. The light was a non flashing one with a two wick oil burner. Sadly, for the lighthouse keeper, technology did away with his job in 1927 when this light was replaced in December 1927 with an “unwatched acetylene with a carbide generating plant attached to the station”. The light was later converted to electricity in 1969. It must have been a great place to live.

The lighthouse keeper’s house has a spectacular view across the Lough. Its built of local rubble stone masonry, this building retains its early form and character. Its visual appeal and expression is enhanced by the retention of much of its original fabric including timber sliding sash windows. Both the house and the lantern were built by McClelland & Co. of Derry. The simple outbuilding and boundary walls are very elegant too.
The views at Dunree are spectacular. Lough Swilly is quite majestic, even on an overcast day. Perhaps, it’s particularly dramatic on a overcast day with the shifting light and colours. You can walk up Dunree Hill and look over towards the Urris Hills and Dunree Bay (Crummies Bay).
There is a regular bus service from Buncrana, a coffee house, museum and public toilet. It might be a good idea to go before they start work on revamping the place!
See more paintings of Inishowen Peninsula here
Read More
https://www.buildingsofireland.ie/buildings-search/building/40901824/dunree-fort-dunree-donegal
https://www.govisitdonegal.com/blog/january-2024/between-waves-and-war

Termon House is set above a pebble beach at the north end of Maghery Strand on the West Coast of the Rosses area of Donegal. The elegant white house was most likely built by the Marquis Conyngham or by his predecessor, Montgomery in the 1770’s for the land agent, whose duty it was to collect rent from the local tenants on behalf of the absentee landlord. A Jamaican-born man named Ralph Spence Philips, was in occupancy at Termon House in the 1820s.
In 1822 the previous years extremely wet weather rotted all the potatoes in the area which resulted in famine. This was happening across Ireland and around a million individuals came to depend upon government aid during this particular crisis. Government agents in Dublin Castle allocated funds for acquisition of foodstuffs in Ireland, to be distributed to the poor at reduced prices or without cost, and to finance local relief works, such as roads, canals and harbours, or other projects deemed of benefit.
It may well have been Philips who initiated the building of the Famine Walls around the property as a means of feeding the local starving population, although he had no tenants of his own. The Public Works Committee in Dublin Castle, however, rejected Philips application for reimbursement and this meant a personal loss to him of £1500 from paying the labourers at a rate of 1d per day!
There is another theory, however, that is that it was the Reverend Valentine Pole Griffith, the Protestant Rector at the height of the Great Famine, 1845-1850, who had the walls built. The Rev Griffith was one of the leading members of the Famine Relief Committee, who worked heroically on behalf of the poor. He set up public works in Maghery, would attend meetings all over the Rosses and write to anyone who he thought could help. The land around Termon House was owned by the Church of Ireland it may well be he who arranged for the massive walls to be built along the road there. On the day we visited it was overcast and my photos do not to justice the scale and extent of the walls.




You can see the famine walls on the right hand side of the house and to the far left side of the outhouses in my painting of Termon House (below). The rocks in the foreground are natural part of the rocky Rosses landscape.
What is undisputed is that this extraordinary and extensive system of walls standing approximately three metres high (10 foot)! The extensive system of tall walls built during this famine around his land is a testament to these hungry builders as they have withstood over 190 years of Atlantic storms.
Today, beautiful Termon House is leased by the Irish Landmark Trust and is available for holiday rental.





More Information
See my paintings of West Donegal here

Summer in Donegal is full of light. Even if its damp summer there is still lots of light. The northly latitude sees to that. It only seems to get properly dark for a couple of hours after midnight and dawn comes impossibly soon. So its great for painting and getting out and about but the light is not so interesting for photography or sketching, especially if, like me, you like lots of strong shadows. So my paintings are usually based on images that are captured in the autumn months. Otherwise, mornings and evening are best for interesting colours and shadows.
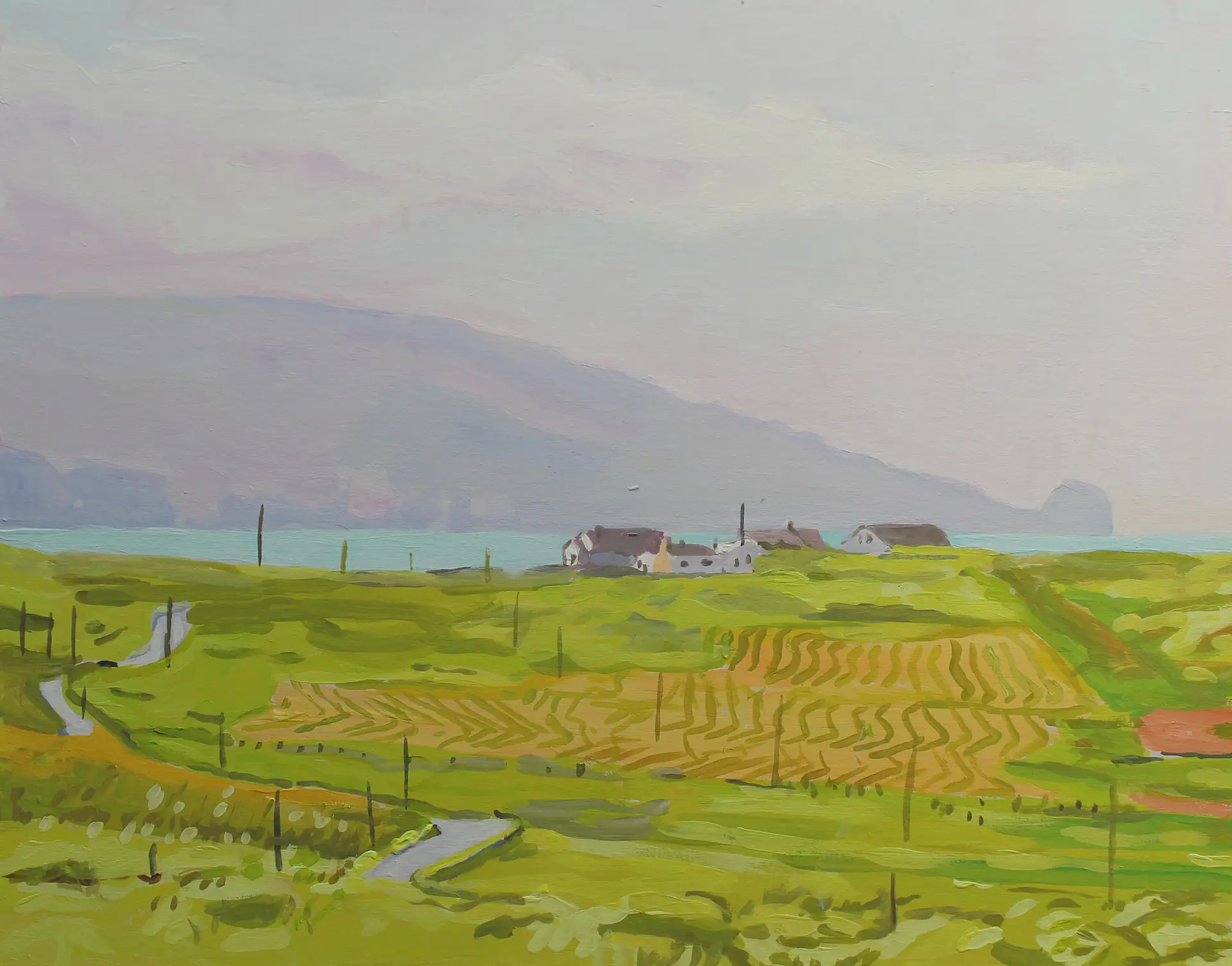
Cruit Island is one of my favourite places in Donegal. It’s rocky and sparsely populated but is accessible by a handy bridge.
We have driven past the collection of farm buildings at Cruit Lower many times but I only managed to capture an image I liked enough to paint this spring. It was an uncharacteristically warm and sunny run of days this May.
The farm has long fascinated me as you have to drive through it. These through roads through farms are not unusal in rural areas in Ireland (and Wales). Informal tracks through a collection of farm buildings, now divided by tarmac.
Lower Cruit was for sale last year and I had a good look at it online. It was interesting as you can only glimpse some of the buildings from the road. I cant remember how much the asking price was. Getting on for a million Euro, maybe. Way out the reach of a poor artist! You got a lot for that; a collection of beautiful historic buildings (some pre-famine era) and access to a beautiful beach and some really incredible views of the West of Donegal. Here are some of the photos from the website. I dont know who bought it but I really hope they look after the beautiful old buildings.
More information about Cruit Lower
https://www.buildingsofireland.ie/buildings-search/building/40904015/cruit-lower-co-donegal
1901 census information http://donegalgenealogy.com/1901cruitlowr.htm
https://www.donegalcottageholidays.com/cruitisland-cruitisland
https://www.booking.com/city/ie/kincaslough.en-gb.html

I am delighted that Peter Zantingh, a Dutch blogger, wrote this an account of Gola and my work. I have translated it for you to read (well, Google did). You can read the original here.
“In the autumn of 2018, Emma Cownie looked out from the Irish mainland at an island she could not get to. It seemed so close. She could see the rocks off the coast and beyond them, scattered seemingly at random across the rolling land, the whitewashed cottages. Some were abandoned, others clearly still inhabited, or used as summer homes.
Gola Island is one of 365 islands off the Irish coast. It is just two square kilometres in size. No one knows exactly how many people live there, because there are more in the summer than in the winter. Ferryman Sabba only goes up and down between June and September.
But in 2022, there were fifteen people living on Gola, according to official figures.
Emma Cownie is a British artist. She studied medieval history at Cardiff University and taught at a secondary school for a while. On 29 February 2012, she was hit by a car. It was, in retrospect, what prompted her to take up painting full-time. The days in front of the class were exhausting, almost all contact with other people in fact, she was startled by every sudden sound. A few years before the accident her dog had been run over on a busy road.
Painting helped.
In the days after she had stood on the mainland looking at those houses in the distance she painted Spring Light on Gola. It came, she told me, ‘out of a kind of longing for the island’.
In the spring she went again. It was early April, sunny but chilly, a cold wind blowing along the coast. Her husband Séamas was with her, their dog Mitzy too. To get the best view of the island – again there was no ferry – they walked along long stretches of beach and climbed on granite boulders, almost pink in the spring light. From here she could see the houses that had recently been renovated and modernised.
That summer she was finally able to go there. ‘There are hardly any cars’, she told me about it. ‘Just a few tractors, no telephone poles or electricity pylons and only a few other people. Other than that, just birdsong and wind. It’s bliss.’
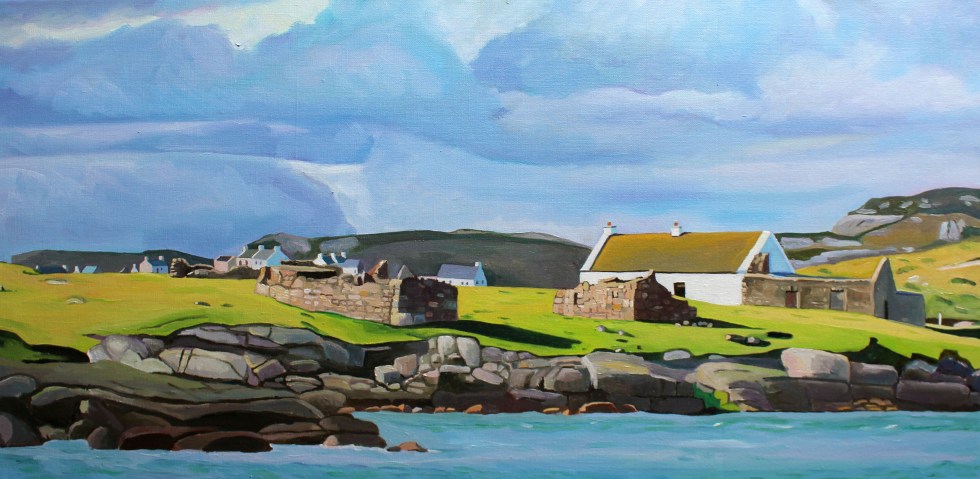
*I emailed Emma Cownie last month with a simple question. One of her paintings was used on the cover of one of my favorite books, Foster by Claire Keegan. I wanted to discuss that book in my newsletter, and I would like to show that painting as well. Would that be okay? I would mention her name and link to her website.
She responded the same day, and we got to talking. She said that the painting I had asked about was called Traditional Two Storey House, Gola, and that it was nice to hear from someone from the Netherlands, because although she regularly sees Dutch campers in Donegal, the county in the northwest of Ireland where she lives part of the time, she has never sold work to anyone from the Netherlands.
The title of the painting made me curious. Gola? What was that? That’s how I became fascinated with the island in my own way.
At one time, there were about two hundred people living there, who made a living from fishing and small farms. But after 1930, the population began to decline. Especially in the winter, it was easier to earn money in the cities, especially those of Scotland and England, and fewer and fewer people returned for the summers. In 1966, the island’s school closed; with only nine pupils (there used to be sixty), it no longer had a right to exist. The few families with young children were forced to move to the mainland – and once the last family with children had left, the community was doomed.
I read this last in Gola: The Life and Last Days of an Island Community (1969) by F.H. Aalen and H. Brody, which I ordered for a few euros on boekwinkeltjes.nl or Abebooks. I think I mainly wanted to know what happened when the last ones left. How does a group of people dissolve itself?
Brody, a sociologist who wrote the part about the last days of the community by the two authors, saw a kind of laconic group feeling among those who were still there at the end of the sixties. Everyone wanted to stay, if the rest stayed too. Everyone thought it was okay to go, as long as everyone else went too.
The most intriguing aspect of each islander’s account of his own predicament is his insistence that it all depends on the others. […] The general attitude is one of wait and see – what the others do. But all of the Gola people are waiting on one another in this way, and do not seem to mind the impasse that this conditional planning involves. Of ten islanders who related their plans, nine said they would like to stay, but it depended on the others. One man said he would stay so long as he had a dog with him, and could not see any advantage to life away from the island. Apart from that one man, all stated they would be glad to remain on Gola, but did not really mind leaving.
The authors also contributed to a short documentary for the Irish public broadcaster RTÉ from the same year, which shows how one family, the O’Donnells, leaves the island. They lock the door and walk with their dog, a long-haired collie, to a motor boat in the harbor. They are all wearing black. (Screenshots from the film below)




Five people remained: fisherman Eddie, fisherman Tadhg, postman Nora and her husband John, and ninety-year-old Mary. It would not be long for them either.
What was left behind? The island had no shop, no pub, not even a church. “The islanders worship on the mainland when the weather is good enough to make a safe crossing,” Brody wrote in 1969. Just over thirty houses remained, most in poor condition. The schoolhouse and the post office. Wooden boxes and fishing nets in the harbour, where a statue of the Virgin Mary, housed in a stone shrine, continued to look out. Two pegs on a washing line.
Between 1969 and 2002, Gola was an uninhabited island. In Dances With Waves: around Ireland by Kajak (1998), Brian Wilson (not the Beach Boys guy, another Brian Wilson) writes about the time he went ashore during his nearly two-thousand-mile kayak trip all the way around Ireland. He hoped to find some peace and shelter that day, but he encountered “the eerie atmosphere of a ghost town”. Fishing boats lay rotting in the harbour among the washed-up debris.
But he found something more hopeful in the cottages. They were “abandoned, but not in decay”.
[…] one felt as though, like faithful dogs, they were just waiting for their owners to return. More than that, it was as if the island itself was still waiting. And the people came again. They came back. Somewhere around the turn of the millennium, the first ones crossed. Today, most of the cottages are still uninhabited, but in summer the sounds and movements of people join those of the cormorants, guillemots and gannets.
Emma Cownie has made more than 25 paintings of Gola in recent years.
For Traditional Two-storey House, Gola, the painting that made me contact her, she returned to the ‘rules’ she had set for herself a few years earlier. These rules – not coincidentally – coincide with how she wanted to organise her life after the car accident and the difficult time that followed: no cars, no people, bright light.
Furthermore, there must be shadows, preferably diagonal, in simple shapes. The painting must be about the interplay between shadows and man-made constructions, the tension between 3D buildings and 2D shadows.
She also wanted to think longer and better about colour. Not to choose the brightest colour, purely for effect, as she had done before, but to work more subtly. In a new series of works based on the houses on Gola Island, including Traditional Two-storey House, she resisted the urge to make the shadows very dark, the sky pale pink and the grass yellow and bright green. “I tried to keep the shapes and colours as simple as possible without it being a cartoon,” she told me. “I wanted to capture the essence of the place.”

She painted the picture in January 2021, during a Covid-19 lockdown in Wales, where she was then living. That summer, she and Séamas moved to Donegal, in the north of Ireland.
It was the following summer, 2022, that she was approached by the prestigious London publishers Faber & Faber: they wanted to use Traditional Two-storey House for the cover of Claire Keegan’s Foster, originally published in 2010.
“I didn’t realise what an honour it was until I got a copy of the book and read it,” she said. “I cried at the end.”
Is there a writing lesson in this? I don’t know. Maybe that there’s more to everything. Maybe it’s worth following your interests and fascinations without reservation. To notice it – this interests me, this grabs me – and follow that line, see where it takes you.

We have been exploring Malin Head a fair bit recently. I really enjoy it’s wildness and dramatic beauty. It’s one of those rare places that is quiet. By quiet, I mean a lack of human busyness. There’s plenty of nature noise like the wind, the hissing of the grasses and leaves as they are blown.This has to be one of the most exposed spots in Ireland.
There is good scattering of robust cottages and relatively few cars. The narrow, winding roads mean that they are not pelting by. Its the quiet and still I hunger for – even when its blowing a gale! The fresh air here is like a refreshing drink of water.
Here are two new Malin Head paintings. The first is “Midsummer at Malin Head” which is a sturdy cottage surrounded by vigorous growths of monbretia. We are a bit early for its distinctive firey orange flowers – the come out from July to September.
The second painting is John’s Cottage, Malin Head (photography with permission of John Gallagher). John was born in the cottage but he now lives with his family (and dog) in a neighbouring cottage a stone’s throw from here.
In the distance are the Urris Hills, also on the Inishowen Peninsula. We spent two days last autumn there, looking for my husband Séamas’s drone crashed on Croaghcarragh (a peak between Urris Hills and Mamore with Mamore Gap in between) after he flew it backward into the mountainside! I spent a longtime waiting for him as various spots on the mountain, looking out towards Dunduff, Clonmany and Malin. The view was magnificent in that direction too. The howling gale that threatened to blow us off the mountain was pretty sobering. Fortunately, the drone was found and it still worked after a night out in the wilds. DJI make pretty tough little drones!
Summer Post-Script
For those who cannot not make it to West Donegal, here’s a brief video of my viewing gallery all set up by Séamas.
If you are thinking of visiting here’s a google map of our location
More Information on Inishowen

Star of the BBC Shipping Forecast
The name will be familar to British ears who ever listened to the daily shipping forecast on BBC Radio. It is broadcast late at night just before 1 am and very early (5.20am). Anyone who is a night owl or insominiac will have listened to it. The list of shipping zones and forecasts is not only practical but also poetic and rather mysterious. Following the litany of locations and numbers is very soporistic. Listen to the clip below. The actual broadcast is from 2.46 onwards ZZzzzzzzzzz
Many British people may not know where Malin Head it is anymore than than they know the location of German Bight or Viking. To Irish ears, however, it is well-known as the most northerly tip of the island of Ireland and also features on Met Eireann’s, sea area forecast, broadcast on RTE.
Malin Head to Mizen Head
People regularly tranverse the length of Ireland from Malin Head, Donegal, to Mizen Head, Cork. It’s a fair stretch. Just under 400 miles (640 km). Some incredible people have cycled it in just over 15 hours. Ordinary mortals take about 4 days.
Amazingly some super-human runners have done it in about the same time – 4 days! I recently listened to a radio interview with the heroic Sophie Power. Sophie is from England and she recently ran the length of Ireland in under 4 days. This is a World Record. She beat the previouis record by three hours. Being a mother, she had to fit it in during her children half-term holiday and didn’t get to pick the day with the nicest weather – just the Tuesday of half-term and so she started off in driving rain! Many years ago I used to run (only piddly 10ks and 5ks) and I would certainly prefer to run in rain than heat.
Incredibly Sophie ran most of the distance without sleep, snatching the odd half an hour on her second and third day. She ended up hallucinating, and with a knee injury that had to be braced. When she finished the race in Cork she had developed heat stroke! That alone shows you how far south Cork is. There’s no way she’d get heat stroke in Donegal! She’s planning to come back and run the Cork Marathon.
At the Edge of the world
Standing at Malin Head is like standing at the edge of the world. To the north is nothing can be seen but sky and sea. A long way off is Iceland and much. much further away to the north-west is North America. It feels very remote (but surprisngly accessible from Letterkenny and Derry/Londonderry) but to fishermen and sailors, I’m sure it’s not. Scotland is surpisingly close to the north-east. If you have ever flown from England to Belfast on a clear day, you can see the Scottish Isles and the Isle of Man scattered across the Irish Sea, pretty close the Antrim coast. Donegal is just a bit further along.

Lookout on Malin Head
On the most northerly tip of the island of Ireland, you will find a tower that was built in 1805 during the Napoleonic wars as a lookout tower to defend against any attacks by the French. You can see at the top left hand side of my painting above. Edges of places are places to look out from – for invaders, or for incoming storms. Weather reports that were important to local and international shipping were first recorded at Malin Head in 1870. It was in that year the tower became a signal tower for Lloyds of London. Semaphore was used to connect with ships at sea and the lighthouse on nearby Inishtrahull. In 1902 the first commercial wireless message was sent from Malin Head to the S.S.Lake Ontario by the Marconi Company.
Divers’ magnet
There are the wrecks of many ships lying off the coast in this area. Many of these such as SS Audacious, SS Carthaginian and RMS Justicia date to the time of the First World War, when Ireland was still part of the British Empire.
In 1917 two German mines sank Laurentic and although her crew successfully abandoned ship, but 354 of them died of hypothermia in her lifeboats.Interestingly, Laurentic was carrying about 43 tons of gold bars when she sank. Most of the 3,211 bars were salvaged by 1924; three more bars were found in the 1930s, however 22 gold bars have still not been recovered.The Great Emergency/Second World War
During the Second World War, Ireland was neutral. The Irish army built lookout posts in places along the coast to prevent any violation of this neutrality. This was important as this part of Donegal is so close to Northern Ireland, which not not neutral and was bombed by the Germans. There is an EIRE 80 sign built of stones during the war so aircraft would know that they were over Ireland (not Northern Ireland). They acted also as a navigational aid for pilots. Eire 79 is at Fanad Head to the west. Eire 81 is at Glengad Head, further along the Inishowen Peninsula, to the east. You can see it on the map below. The SS Athenia, a passenger ship carrying 1,418 people was torpedoed by a German U-boat just hours after war had been declared in 1939 off the coast of Malin Head! Most of the passengers survived but 117 perished.

Some scenes from the film Star Wars: The Last Jedi film was shot at Malin Head. I have to admit that I am not a Star Wars fan – I never made it through awhole film. I have to admit that I’m more of a Star Trek fan. Apparently, it is possible to have a tour of the locations used for the film from local tour guides. The road leading up to Bamba’s Crown has been renamed locally from the R242 to the R2D2 in recognition of the Star Wars connection. Also beside the tower, there is a short lovely refreshing walk along the cliffs to Hell’s Hole. The cliffs are massive here and even on a relatively calm day the sea is restless and a bit intimidating It needs to be remembered that this not just a sea here but an Ocean.

Read more
https://www.inishview.com/activity/the-tower
https://www.authenticvacations.com/star-wars-filming-locations-ireland
https://www.odohertyheritage.org/maps

There is a unique architectural gem, perched upon the high cliffs above the shores of the north Derry coastline. It is an elegant Roman-style round temple; a beautiful rotunda. It is a wonderful surprise. There is none other in Ireland. It looks out across Lough Foyle to Donegal to the north and on a clear day the Scottish Isles can be seen to the north-east. This remarkable building is Mussenden Temple.
It was built by the eccentic and extravagant Earl Bishop of Derry, Frederick Hervey (b.1730-1806). The 18th century is full of mischievious and surprising characters and he’s one of the best. Frederick Hervey was in turns controversial, revolutionary and yet both shocking and popular in his own life time. He came from an aristocratic English family, the 3rd son of an earl with big estates in Suffolk. Having two elder brothers he probably never expected to inherit from his father. He first tried law and then became a vicar hoping for a career in the church. His family connections helped a lot. He became chaplain to the king, George III in 1763, who later called him ‘that wicked prelate’ .
When his eldest brother George became Lord Lieutenant of Ireland in 1766, he managed to wangle the post of Bishop of Cloyne for Frederick and then, shortly afterwards, in 1768, Bishop of Derry, one of the wealthiest Irish sees.
Frederick threw himself into being Bishop of Derry, reportedly visiting every parish in the diocese and embarking on a number of notable building projects in the city of Londonderry including building St Columbs Cathedral’s first spire (it had to be replaced later as it was too heavy) many fine building and the first (wooden) bridge over the River Foyle, earning himself the nickname ‘the Edifying Bishop’.
In 1779 his brother George died and Frederick became the 4th Earl of Bristol, inheriting an income of £20,000 a year. He now even more money. He spent a fortune on building and collecting art.
He was widely travelled and had a fine appreciation of art, especially Greek and Italian. He spent 18 years of his life in Italy and spoke Italian fluently. Frederick was also well-read and he was an expert in flora and fauna and publicised The Giant’s Causeway. The Earl Bishop did extensive research into the origins of the Causeway and promoted his findings to the scientific community and wider world.
He also visited Staffa Island on the Western Isles of Scotland to confirm the links with similar columnar formations. In 1782, he was made a Fellow of the Royal Society for his efforts.
The Earl Bishop was a colourful character and was clearly someone people loved to gossip about. There are many examples of his eccentricity. It is said that he made his clergy run a leapfrog race on Downhill beach to see who would win the best area!
He had an eye for the ladies and was reputed to have had several affairs. Among his mistresses was society beauty Madam Ritz, as well as possibly Emma Hamilton who was also the mistress of Admiral Lord Nelson.
It was on his tour of Europe that he fell in love with Bramante’s Temple in Rome. He reportedly tried to buy it and have it moved back to Britain but the Pope would not let him. So the Frederick Hervey built his own. Several of them. He built Ballyscullion, near Bellaghy, Co Derry, in 1787 to his own extravagant designs. The façade was inspired by St Peter’s in Rome, and measured 350ft across, with a central rotunda flanked by curved wings and a large pavilion at each end. It sadly, no longer exists.
He also started Ickworth House, in Suffolf in 1795 which was completed by his successors.
His first rotunda, however, was Musseden Temple, built in 1873. It was built as a library on the cliff edge of his estate at Dunbo, County Londonderry, Northern Ireland. Dunbo derives from the Irish Dún Bó, meaning ‘fort of the cows’. Dunbo was renamed Downhill Demense and an incredible 300,000 trees were planted on the estate; although there is little sign of them today.
A huge castle was built with the assistance of number of architects (Frederick kept firing them) including Michael Shanahan of Cork and Placido Columbani of Milan, who was supervising plumbing and the installation of water closets, a swanky innovation for the time. So we are not entirely sure who designed the rotunda/temple on the cliffs.
The temple was dedicated to his lovely young cousin Frideswide Mussenden (neé Bruce) who had recently married the rich banker, Daniel Mussenden, had given birth to a child. The temple was meant to a be delightful retreat for her to escape to and look out at the wonderful view or read some of the many books there. A fire was kept lit at all time to save the books (and her) from the damp Irish weather. Sadly, Frederick’s terrible reputation with women meant that their “friendship” was gossiped about, in the press. The fragile Frideswide was horrified to be written about in the Freeman’sJournal, even if she wasn’t mentioned by name, and it may well have supposedly sent her into a physical decline, dying at the age of tender age of just 22 in 1785.
There is a minature of her in the National Gallery of Ireland painted when she was 17 in 1780, presumably when she had just married Daniel. She has a very sweet and tender face; you can easily imagine her upset at the nasty rumours.
So the library on the cliffs is a poignant place. Built for a young woman who perhaps only used it for a short time before she died. It was always close to the cliff edge, reported 30 foot away when it was built. I think that is an exaggeration, as maps from the early 19th century do not show that much land between the temple and the cliff edge. The cliff has eroded and about 20 years ago the National Trust did extensive work to stablise the cliff and underpin the temple.
I am very bad at remembering to take work in progress photos of my work. I often get too caught up in painting the piece. I am also usually very anxious about a painting until I have practically finished it!
This is a painting done with acrylic paints. I work with thin layers of paint, building up the colours and adjusting them, lighter or darker with each new layer. Often I like the painting best when its about a third done – I am confident I know where I am going with it and it still has “potential”.
Here there are still some “problems” to solve, the shadow on the temple needs to be darkened.

Frederick Hervey was a fascinating man, who had a long and varied life and I could write a lot more about him. He was minor celebrity in his day, he travelled widely on the Continent, where he kept company and correspondence with leading philosophers, princes, politicians, scientists, artists, architects and writers—including Voltaire, Goethe, Benjamin Franklin, John Strange, Jeremy Bentham, James Boswell and the Pope. He has been described as “a bad father, and worse husband, a determined deist, [who was] very blasphemous in his conversation”.
Yet he was a generous man who treated the people of Derry well, whether Catholic, Protestant or Non-Conformist (a type of Protestant that was discriminated against by the state at the time). He argued all his life for religious tolerance.
He believed the answer to the Irish question or the Irish problem of a disaffected Catholic majority is, was not meanness but generosity. Just as God wins our prayers of thanksgiving by His extravagant generosity, so England could learn how to win over Irish Catholics by giving them more, not less. He bankrolled the first Catholic chapel in Derry—Long Tower Church—and personally chose the magnificent Italian marble that adorns the altar.
He undertook public works to relieve poverty, and was a generous patron to the Catholic population of Derry.
He died in Italy in 1803, trying to recover his art collection that had been conviscated by Napoleon Bonaparte. Hundreds of artists attended his funeral in Rome and he was buried at his ancestral home, Ickworth in Suffolk, where there is an obelisk paid for by public subscription by the Catholics, Presbyterians and Protestants of Derry.

Find out More
https://www.nationaltrust.org.uk/visit/northern-ireland/mussenden-temple-and-downhill-demesne
It’s Downhill All the Way
The ‘oral-bishop’: the epicurean theology of Bishop Frederick Hervey, 1730–1803
https://www.earlbishopstrail.com/
https://vipauk.org/enter/muse/ni/i30.html
Click to access EARL-BISHOP-BOOKLET-WR.pdf
Edifying and Eccentric – The Earl Bishop

The Sperrins or Sperrin Mountains (Irish: Sliabh Speirín) are a mountain range in Northern Ireland. The name Sperrin derives from “Na Speiríní ” meaning “Spurs of Rock” and it is the rocks of the Sperrins and the rolling geography of the area that form the foundation of this distinct landscape. The mountain range, stretching 40 miles along the border of counties Tyrone and Derry, is the largest in Ireland. There are 10 summits above 500 metres with the highest of the range, Sawel Mountain, peaking at 678m (2,224ft).
The landscape is mostly moorland and blanket bog. The Sperrins were designated an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty in 1968. It’s a sparse rolling landscape. These peaks have been smoothed out by glaciers thousands of years ago. Populated by sheep, bog grass (Eriophorum angustifolium) and farmhouse, old and new.
Some old farm buildings have long-been abandoned by people but are still used for farm equipment and shelter for sheep. So long as there is a tin roof, the walls will last years and years.

I love the sharp oranges of those tin roofs and I will return to them again and again for inspiration. Broadly speaking, in terms of composition I am looking for three dominant colours; green grass/sky and orange tin roofs. You can see how I simplify these main colours in the painting below.

Drone photography has become widespread in our lives. I remember clearly first seeing drone shots of different American cities in episodes of CSI. They were tracking shots of skyscrapper from directly above. As if you were a bird, flying directly above. They were fascinating. Funny, I cant find a clip to illustrate online now. These days they are used in local and national news and documentaries so frequently I dont think we even register that they are drone shots. They have become part of everyday our visual language.
Recently, I have started to explore the use of drone footage (shot by my husband) to extend the possiblilties of compositions I can paint from. So often, I have thought: “If only I was 20 foot high, I’d get a great shot”. So now I can see from 20 foot above, or round the otherside.
I know that many people think that “real” art is plein air sketching, live and I would need to be in a hot airballon to get these views. I admire people who can do this. I can’t. I am not a plein air painter. I am too much of a control freak. I work slowly in the comfort of my studio with all my paints within arms’ reach, exactly where I want them.
This is the first rainbow I have painted. I was pretty nervous about doing it as rainbows are so beautiful and etheral. They are also fleeting. I am reasonably happy with the result although I would be happier if it was more transulent. If I painted another one I would use more acrylic medium to get a more see through effect.

I can also use drone footage and photography if collectors want a commissioned work with drones offering a novel view of their favourite places! It certainly has helped me become more creative with compositions and has benefitted my work greatly.